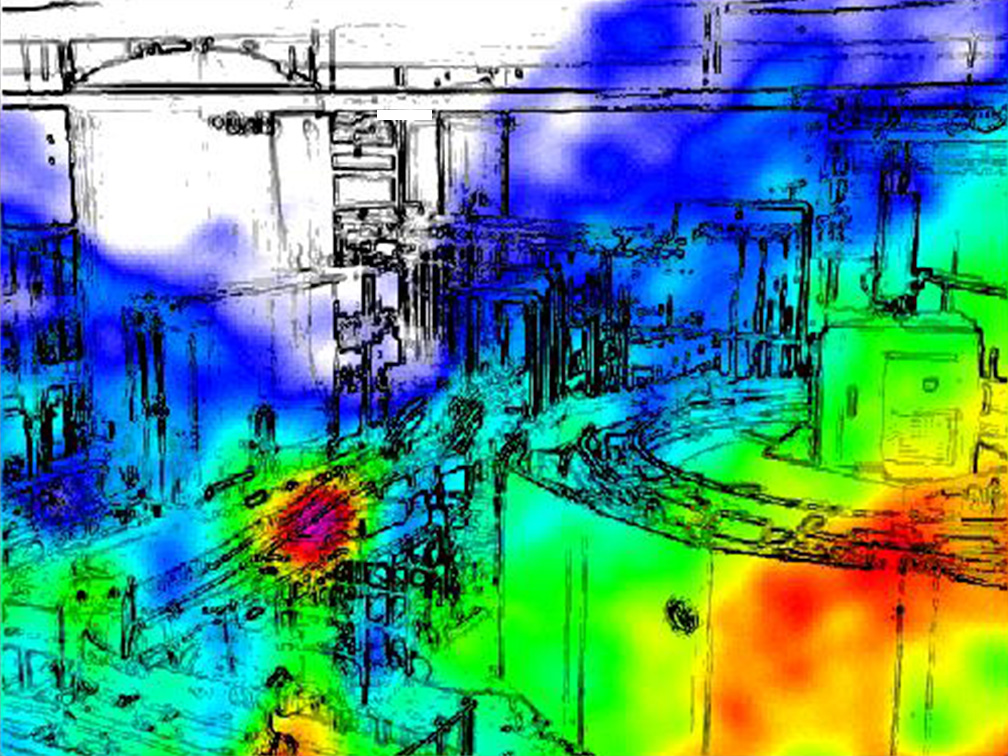
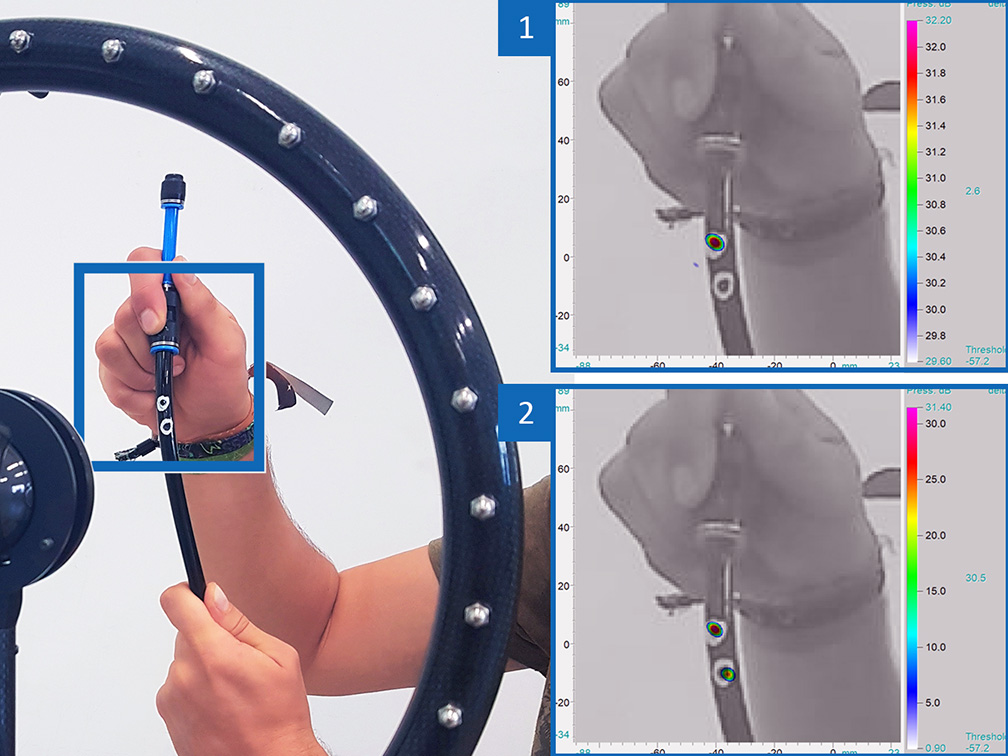
Leakages of pressurized air or other gases are often causing additional costs and can sometimes be even dangerous. Localizing such leakages by ear is normally hard or even impossible because ultrasonic emissions are inaudible by the human ear especially in industrial environments. Here, the Acoustic Camera enables maintenance personnel to accurately detect leakage sounds even far in the ultrasonic frequency range.
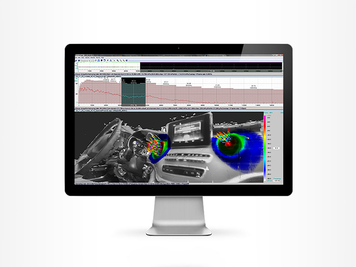
Another application of the Acoustic Camera is in predictive maintenance. While experienced maintenance experts can sometimes hear the difference between a smoothly running machine and a faulty one, they mostly can't properly localize the abnormal sound. Less skilled personnel might not even hear the difference. When using the Acoustic Camera for predictive maintenance and comparing the measurement results to previously recorded acoustic images of "good" machines, differences showing errors and damage become obvious immediately. Corrective measures can be implemented to prevent further damage and downtimes.
Sometimes damages or faulty parts in a machine are noticed by maintenance personnel or internal sensors but can't be accurately localized. In this case, the machine needs to be shut down for lengthy diagnostic procedures or parts are exchanged on a trial-and-error basis. This is a costly process that can be avoided by using the Acoustic Camera to localize and exchange only the parts really causing the malfunction. Defective parts often generate different and louder sounds than good parts. The Acoustic Camera can be used to exactly localize defective parts like bearings, gears, shafts, etc. and help pinpoint the root cause of malfunctions.
- Leakage detection
- Predictive maintenance
- Faulty part localization