The HDR-Algorithm is an algorithm based on beamforming and working in the time domain. Moreover, HDR is an iterative deconvolution technique that increases the dynamic of an acoustic photo and therefore facilitates the separation of sources. Hence, the procedure is especially convenient for signals containing several sources which cannot be identified separately as the difference between their sound pressure levels exceeds the dynamic of the used microphone array.
If the difference between two sources’ sound pressure levels is higher than the dynamic of the microphone array, the quieter source cannot be located compared to the louder one. In this case the sidelobes of the louder source mask the quieter source. In addition, the superposition of multiple sidelobes leads to their interference and therefore ghost sources may occur.
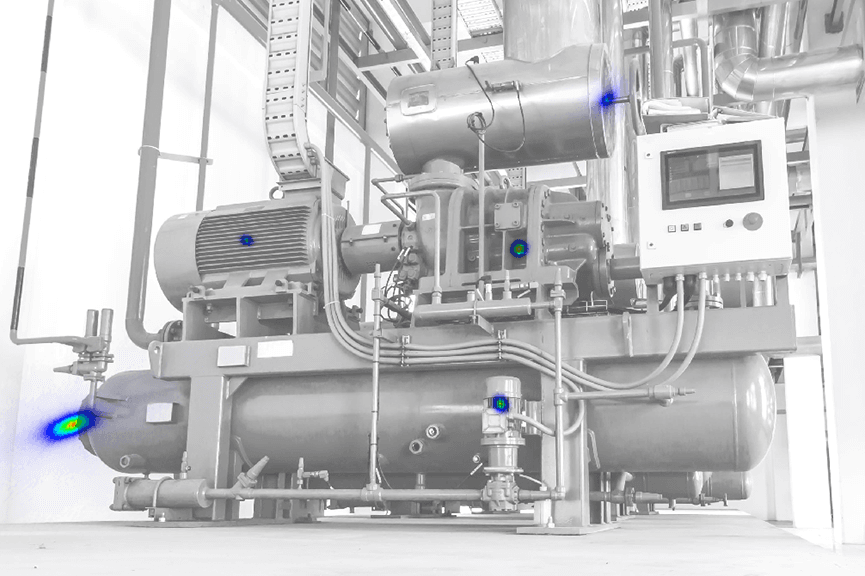
Fig. 1 shows an acoustic photo with TDBF calculated. There are five sources displayed that were simulated at different positions with white noise and sound pressure levels of 90 dB, 80 dB, 70 dB, 60 dB and 50 dB. One can clearly recognize that only the loudest sources 1 and 2 can be located. All the other ones are masked by the sidelobes of these two.
In order to identify the remaining sources as well, HDR needs to be applied to the acoustic photo: In each iteration step the loudest source is removed from the signal using the acoustic eraser and then added to a new, clean acoustic map. Eliminating the loudest source is in the original acoustic photo increases the dynamic to enable the identification of sources outside the detectable range (see Fig. 2).